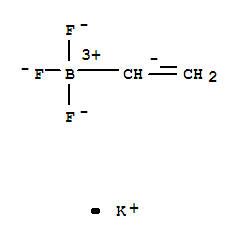
546-88-3
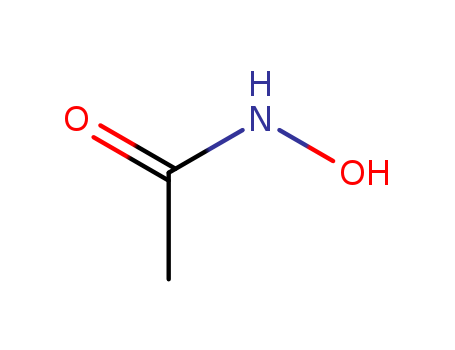
- Product Name:Acetohydroxamic acid
- Molecular Formula:C2H5NO2
- Purity:99%
- Molecular Weight:75.0672
Product Details
Reputable factory supply Acetohydroxamic acid 546-88-3 in bulk at low price
- Molecular Formula:C2H5NO2
- Molecular Weight:75.0672
- Appearance/Colour:White crystalline solid
- Vapor Pressure:0.0118mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:88-90 °C(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.42
- Boiling Point:231.4 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:8.70(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:127.6 °C
- PSA:49.33000
- Density:1.155 g/cm3
- LogP:-0.09740
Acetohydroxamic acid(Cas 546-88-3) Usage
|
Manufacturing Process |
3 Methods of producing of acetohydroxamic acid: 1. Ethyl acetic acid ether was treated with hydroxylamine and acetohydroxamic acid was obtained. 2. Acetohydroxamic acid was obtained in the result of reaction of acetamide with hydroxylamine. 3. Acetohydroxamic acid was obtained by treatment of acetaldehyde with nitrohydroxylamine. |
|
Therapeutic Function |
Urease inhibitor |
|
Side effects |
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.Call your doctor at once if you have:pounding heartbeats or fluttering in your chest;signs of a blood clot in your leg --pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in one or both legs;signs of a red blood cell disorder --pale or yellowed skin, dark colored urine, fever, confusion or weakness.Common side effects may include:headache during the first 2 days of treatment;skin rash, warmth, tingling or redness (especially if you drink alcohol while taking acetohydroxamic acid);upset stomach, nausea, loss of appetite;depressed mood;anxiety, tremors, nervousness;hair loss. |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by intraperitonealroute. An experimental teratogen. Other experimentalreproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heatedto decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. |
|
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments |
Acetohydroxamic acid can be used in dogs as adjunctive therapy in some cases of recurrent urolithiasis or in the treatment of persistent urinary tract infections caused by the following bacteria: E. coli, Klebsiella, Morganella morganii, Staphylococci spp., and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adverse effects limit its usefulness. |
|
Brand name |
Lithostat (Mission). |
|
General Description |
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease activity and reduces urinary ammonia levels. 2-Acetohydroxamic acid loaded floating microspheres forms an efficient drug delivery system for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori. |
InChI:InChI=1/C2H5NO2/c1-2(4)3-5/h5H,1H3,(H,3,4)
546-88-3 Relevant articles
N-O Bond Fission as the Rate-Determining Step in the Aqueous Conversion of N-Peptidyl-O-(p-nitrobenzoyl)hydroxylamines to p-Nitrobenzoic Acid and Peptidylhydroxamic Acids
Demuth, Hans-Ulrich,Fischer, G.,Barth, A.,Schowen, R. L.
, p. 5880 - 5883 (1989)
N-Acetyl-, N-alanyl-alanyl-, N-alanyl-pr...
Investigation of structural effects and behaviour of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase encapsulated in reversed micelles
Fragoso, Ana,Pacheco, Rita,Karmali, Amin
, p. 264 - 272 (2012)
The acetohydroxamic acid synthesis react...
Activation and Orientation by Receptor-Substrate Binding. The Case of Acyl Transfer from O-Acetylhydroxylamine
Lehn, Jean-Marie,Nishiya, Takako
, p. 215 - 218 (1987)
The strong binding ability of the recept...
The reaction of hydroxamic acids with water-soluble carbodiimides. A Lossen rearrangement.
Hoare,Olson,Koshland Jr.
, p. 1638 - 1643 (1968)
-
Hydroxamic acids. II. Kinetics and mechanisms of hydroxyaminolysis of succinimide.
Notari
, p. 1064 - 1068 (1969)
-
Alternating Current Electrolysis as Efficient Tool for the Direct Electrochemical Oxidation of Hydroxamic Acids for Acyl Nitroso Diels–Alder Reactions
F?hrmann, Jan,Hilt, Gerhard
supporting information, p. 20313 - 20317 (2021/08/12)
The acyl nitroso Diels–Alder reaction of...
Hydroxamates as a potent skeleton for the development of metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors
Chen, Cheng,Chigan, Jia-Zhu,Ding, Huan-Huan,Li, Jia-Qi,Liu, Lu,Xu, Yin-Sui,Yang, Ke-Wu
, (2021/12/14)
Bacterial resistance caused by metallo-β...
Novel fluorinated 7-hydroxycoumarin derivatives containing an oxime ether moiety: Design, synthesis, crystal structure and biological evaluation
Dai, Peng,Jiao, Jian,Wang, Qing-Qing,Zhang, Shu-Guang,Zhang, Wei-Hua
, (2021/06/28)
A series of fluorinated 7-hydroxycoumari...
Synthetic method for acetylhydroxylamine
-
Paragraph 0026-0029, (2021/08/06)
The invention provides a synthesis metho...
546-88-3 Process route
-
-
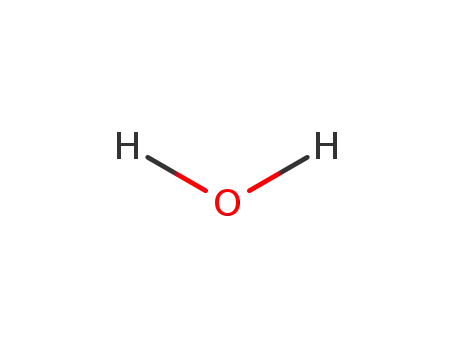
7732-18-5
water
-
-
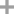
7803-49-8
hydroxylamine

-
-
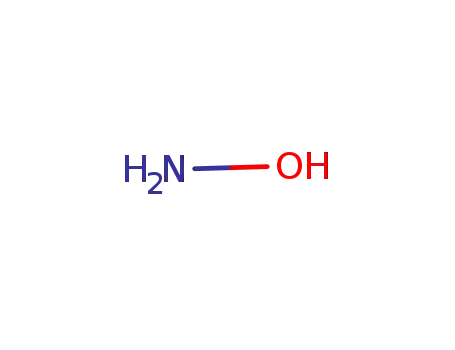
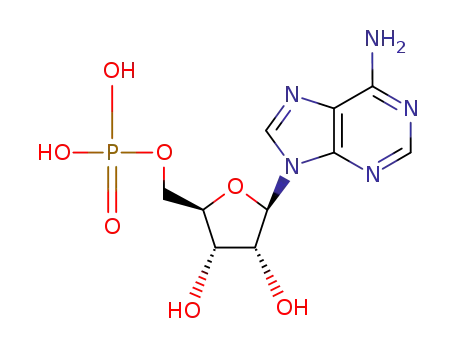
13015-87-7
adenosine-5'-phosphoric acetic anhydride

-
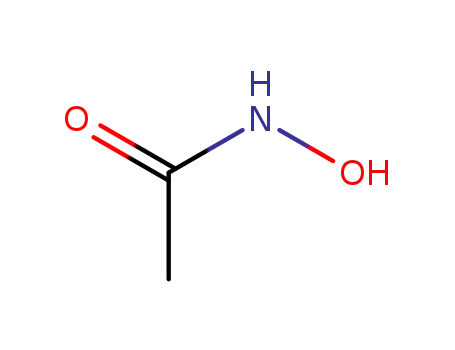
-
546-88-3
acetylhydroxamic acid

-
-
61-19-8,24937-83-5,67583-85-1
5'-adenosine monophosphate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
at 37 ℃;
pH 6; Halbwertszeit der Reaktion;
|
-
-
3354-65-2
N-(1-nitroso-ethylidene)-hydroxylamine

-
-
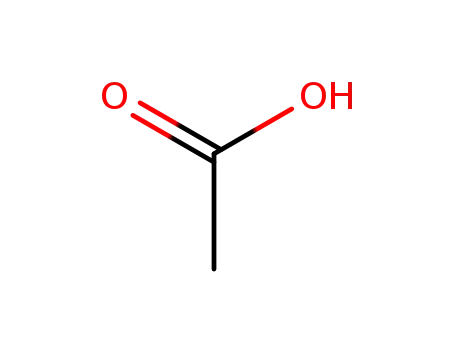
64-19-7,77671-22-8
acetic acid

-

-
546-88-3
acetylhydroxamic acid

-
-
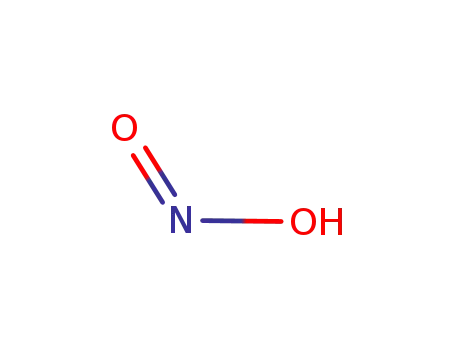
7782-77-6
cis-nitrous acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
546-88-3 Upstream products
-
60-35-5
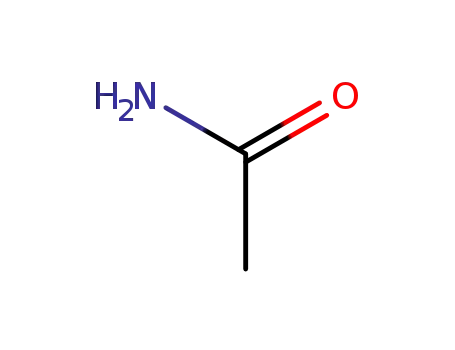
acetamide
-
463-51-4
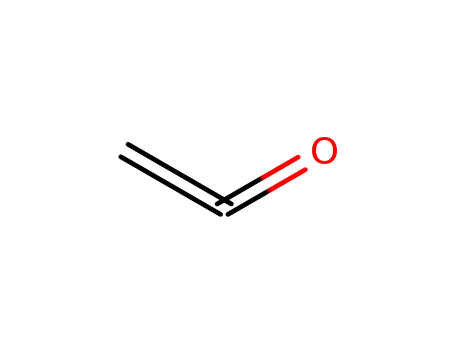
Ketene
-
107-29-9
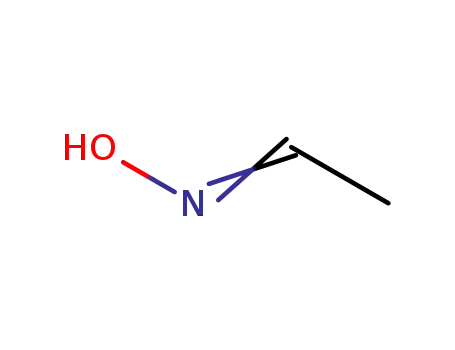
Acetaldehyde oxime
-
79-24-3
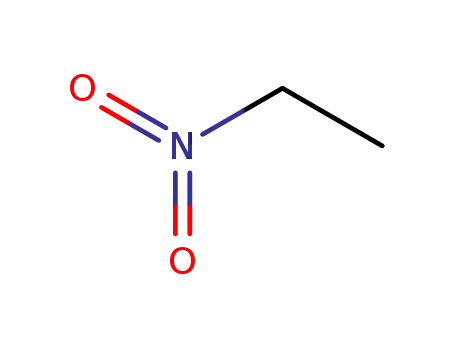
Nitroethane
546-88-3 Downstream products
-
76412-58-3
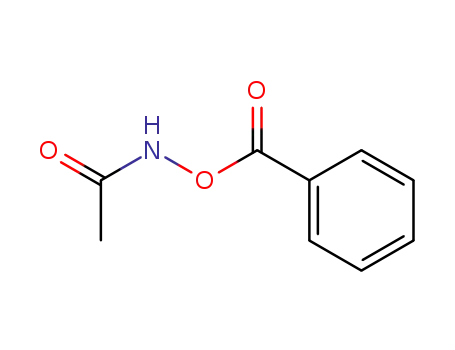
N-acetyl-O-benzoylhydroxylamine
-
70341-55-8
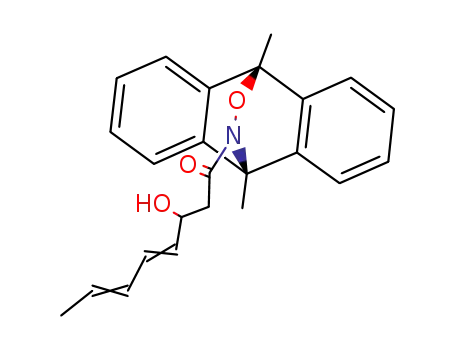
12-(3-hydroxy-octa-4,6-dienoyl)-9,10-dimethyl-9,10-dihydro-10,9-oxaazaethano-anthracene
-
51029-28-8
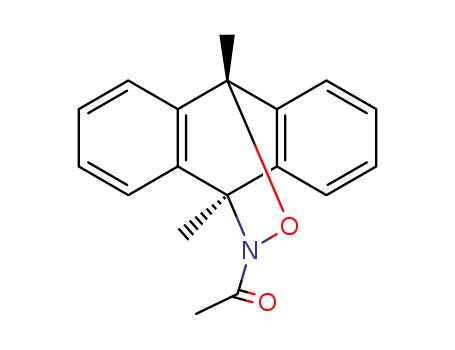
12-acetyl-9,10-dimethyl-9,10-dihydro-10,9-oxaazaethano-anthracene
-
95705-96-7
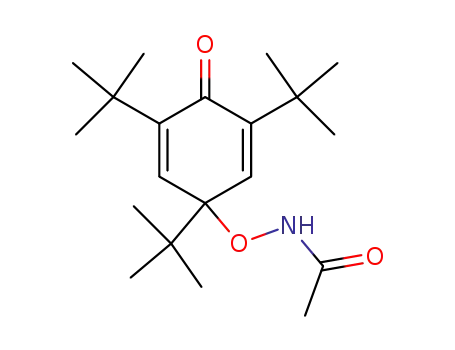
Acetamino-(1,3,5-tri-tert-butyl-4-oxo-cyclohexa-2,5-dienyl)-ether
Relevant Products
-
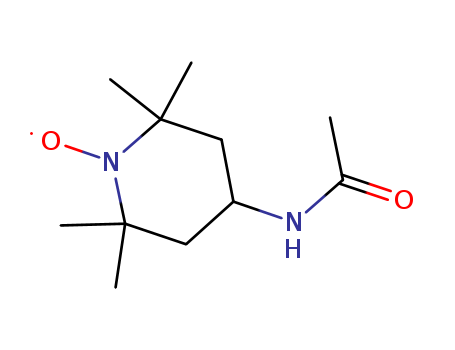
4-ACETAMIDO-TEMPO
CAS:14691-89-5
-
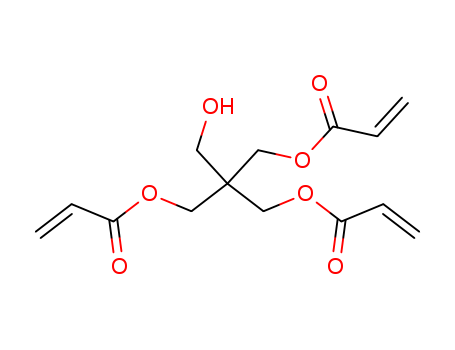
Pentaerythritol triacrylate
CAS:3524-68-3
-
POTASSIUM VINYLTRIFLUOROBORATE
CAS:13682-77-4